Is cloud computing a hot skill in 2026? Yes, definitively. The data shows unprecedented demand, competitive salaries, and a critical skills shortage creating exceptional career opportunities.
Key Statistics:
- Global cloud computing market: $912.77 billion in 2025, projected to reach $5,946.84 billion by 2035 (20.61% CAGR)
- Over 90% of organizations face IT skills shortages by 2026, costing an estimated $5.5 trillion
- Average cloud engineer salary: $130,802 nationally (entry-level $80,000-$110,000; senior roles $175,000+)
- Job growth rate: 25-26% faster than average occupations through 2034
- 317,700 job openings annually in the United States alone
Understanding Cloud Computing in 2026
Cloud computing enables organizations to access computing resources—servers, storage, databases, networking, software—over the internet rather than maintaining physical infrastructure. In 2026, cloud computing has evolved beyond basic infrastructure into an ecosystem encompassing:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Growing at the highest rate, holding 26% market share
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Projected 17.06% CAGR with serverless computing innovations
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Dominant segment driving enterprise adoption
The cloud landscape in 2026 is characterized by hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, with 67% of organizations using public cloud, 55% maintaining on-premises infrastructure, and 45% utilizing private cloud. The integration of AI, machine learning, and edge computing has transformed cloud computing from a cost-saving measure into a strategic competitive advantage.
Market Size and Growth Statistics
Global Market Performance
The cloud computing market demonstrates explosive growth across all forecasting models:
2026 Market Valuations:
- Precedence Research: $912.77 billion (2025) → $5,946.84 billion (2035)
- Fortune Business Insights: $905.33 billion (2026) → $2,904.52 billion (2034) at 15.7% CAGR
- Markets and Markets: $1,294.9 billion (2025) → $2,281.1 billion (2030) at 12% CAGR
Key Growth Drivers:
- AI and machine learning integration requiring specialized cloud infrastructure
- Digital transformation initiatives accelerating post-pandemic
- Hybrid and multi-cloud adoption becoming industry standard
- Edge computing expansion for low-latency applications
- Generative AI workload demands

Regional Analysis
North America dominates the cloud market:
- United States: $523.29 billion (2025) → $3,462.37 billion (2035) at 20.80% CAGR
- Leads in early adoption of AI, blockchain, robotics, and IoT
- Home to AWS, Microsoft, Google Cloud—the three hyperscalers controlling 67% market share
Asia-Pacific shows highest growth potential:
- Fastest-growing region at 18.8% CAGR
- Driven by developing economies (India, China) embracing digital transformation
- Manufacturing and retail sectors leading cloud adoption
Europe demonstrates steady expansion:
- $205.63 billion valuation in 2026
- 16.80% CAGR driven by government initiatives
- EU investment of $1.2 billion in cloud infrastructure projects (IPCEI CIS)
Service Model Breakdown
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
- Highest growth rate during 2026-2034
- 26% market share in 2025
- Driven by reduced initial investment costs and elimination of on-site data centers
- Strengthened by edge computing, AI, and ML workload growth
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
- 17.06% CAGR forecast
- Serverless computing and container orchestration transforming the segment
- Enabling faster application development and deployment
Software as a Service (SaaS):
- Largest segment by revenue
- Growth from $205,221 million (2022) to $243,991 million (2024)
- 15.9% annual growth rate
Job Demand and Employment Data
Quantified Demand Statistics
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics provides concrete employment projections:
- Growth Rate: 25-26% from 2023 to 2033 (significantly faster than the 4% average for all occupations)
- Annual Job Openings: 317,700 positions per year through 2034
- New Jobs Created: 451,000 expected new positions in the next decade
- Computer and Information Research Scientists (umbrella category for cloud roles): 26% employment growth
Skills Shortage Crisis
Multiple research firms confirm a critical talent gap:
IDC Research Findings:
- Over 90% of organizations will face IT skills shortages by 2026
- Estimated cost: $5.5 trillion globally
- Cloud skills represent significant portion of shortage areas
Industry Survey Data:
- 63% of U.S. organizations anticipate IT skills gap widening
- 59% expect talent shortages to continue in coming years
- 81% of U.S. engineering leaders plan to hire abroad due to domestic shortage
- 28% of business leaders prefer contract/freelance workers
Most In-Demand Cloud Roles
Cloud Engineer (Average Salary: $142,987)
- Deploying, maintaining, and optimizing cloud infrastructure
- Day-to-day management of cloud environments
- Highest volume of job postings
Cloud Architect (Average Salary: $147,236)
- High-level cloud strategy design
- Platform selection and cost optimization
- Security and scalability planning
DevOps Engineer (Cloud-Native Focus)
- CI/CD pipeline design and automation
- Container orchestration and monitoring
- Bridging development and operations
Cloud Security Engineer
- Critical due to expanding attack surfaces in hybrid/multi-cloud
- 90%+ organizations facing security talent shortage
- Premium compensation due to scarcity
Cloud Data/ML Engineer (Average Salary: $117,703-$176,611)
- Large-scale data pipeline management
- AI/ML workload integration
- Fastest-growing specialty area
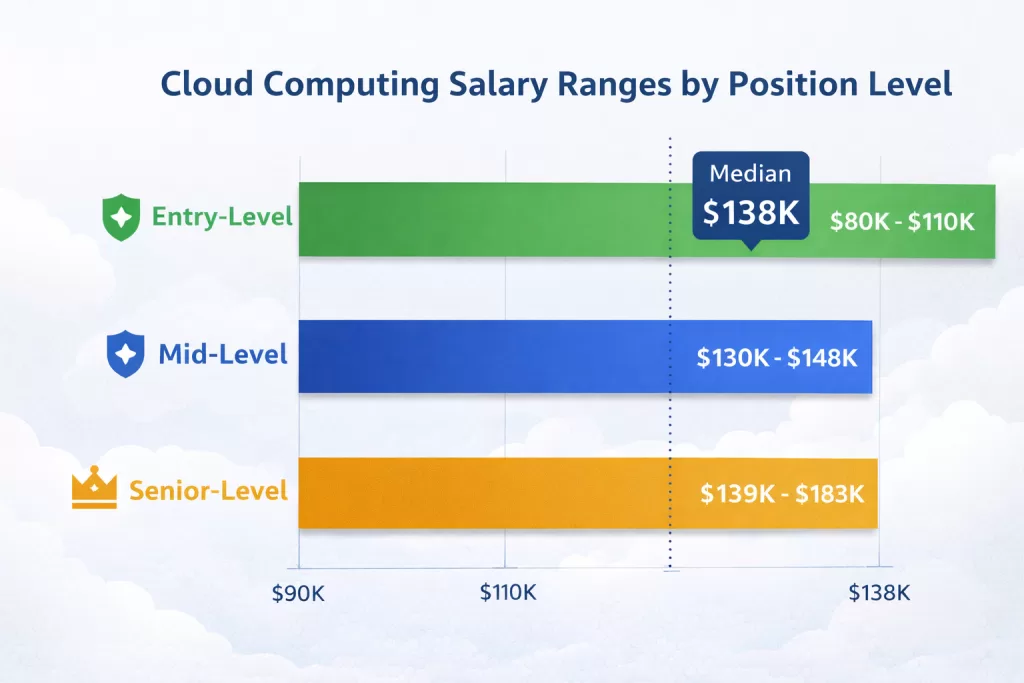
Salary Analysis by Role and Location
National Salary Averages (United States)
Entry-Level Positions:
- Cloud Engineer: $80,000-$110,000
- Average starting salary: $130,802
- Foundational certifications increase starting pay by 15-25%
Mid-Level Positions:
- Cloud Engineer: $130,000-$142,987
- Solutions Architect: $140,000-$147,236
- DevOps Engineer: $120,000-$145,000
Senior-Level Positions:
- Senior Cloud Engineer: $139,000-$183,000
- Cloud Architect: $147,000-$175,000
- Cloud Security Specialist: $155,000-$182,000
Median Total Compensation:
- National median: $138,000 (includes base salary plus bonuses, profit-sharing, commissions)
- Certified professionals earn 25-40% premium over non-certified counterparts
Industry-Specific Salaries
Finance & Insurance (Highest-Paying Sector):
- Cloud Engineer: $122,891-$128,175
- Driven by security requirements and regulatory compliance
- Premium for handling large-scale transactional data
Technology Sector:
- Cloud Engineer: $114,509 average
- AWS, Microsoft, Google offer highest compensation
- Stock options and equity significantly boost total compensation
Healthcare:
- Cloud Engineer: $111,000-$122,000
- Rapid growth due to telehealth and digital patient records
- HIPAA compliance expertise commands premium
Geographic Salary Variations
Top-paying U.S. cities for cloud professionals demonstrate significant location-based premium:
High-Cost Tech Hubs:
- San Francisco Bay Area: 25-35% above national average
- Seattle: 20-30% premium
- New York City: 20-25% premium
- Boston: 15-20% premium
Emerging Tech Markets:
- Austin, Texas: Competitive with established hubs
- Denver, Colorado: Growing cloud talent concentration
- Atlanta, Georgia: Emerging Southeast hub
Cost-Adjusted Value:
- Remote positions maintain geographic salary differentials
- Hybrid work models enable geographic arbitrage
- Smaller markets offer better cost-of-living adjusted compensation
Certification Impact on Salary
AWS Certifications:
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Professional: ~$160,000 average
- 30-40% salary increase over non-certified
- Professional-level certifications command highest premiums
Azure Certifications:
- Azure Solutions Architect Expert: ~$140,000 average
- Strong demand in enterprise environments
- Microsoft ecosystem expertise highly valued
Google Cloud Certifications:
- Professional Cloud Architect: ~$155,000 average
- Highest-paying cloud certification category
- Data and AI specialization commands premium
Industry Adoption Rates
Cross-Industry Cloud Usage
Overall Adoption Statistics:
- 96% of companies use public cloud services
- 84% utilize private cloud infrastructure
- 80% operate multi-cloud or hybrid strategies
- 62% of SMB data stored in cloud (63% of workloads)
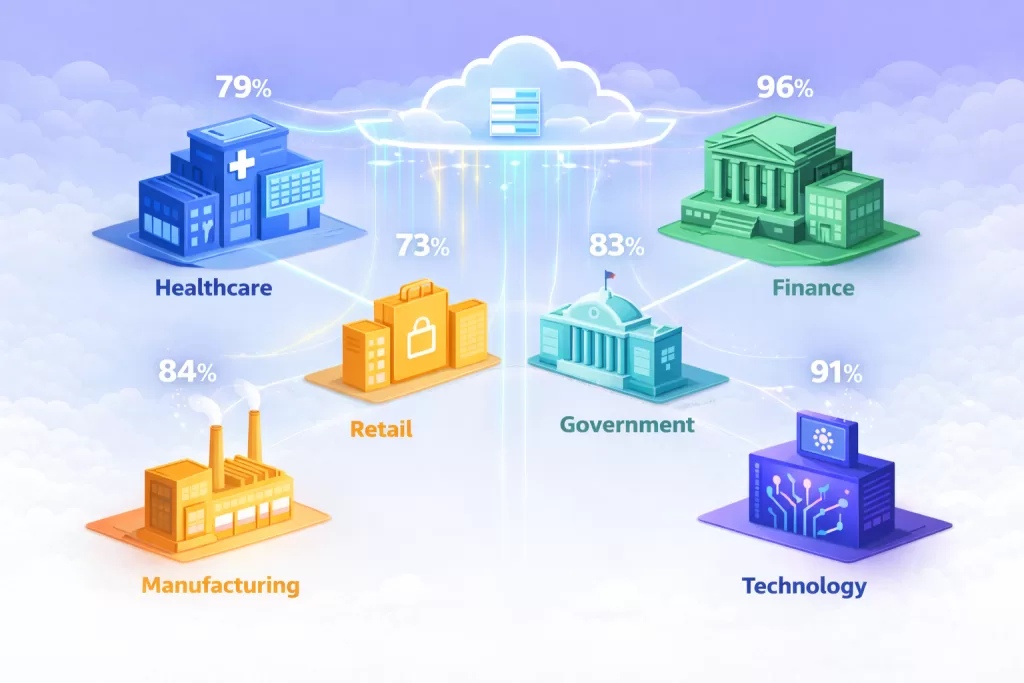
Sector-Specific Adoption
Banking, Software & Telecommunications:
- Combined $326 billion public cloud spending by 2027
- Leading spenders driving market growth
- 81% of insurers use cloud for claims management
Retail & E-Commerce:
- Highest cloud usage at 79%
- Digital transformation imperative
- Inventory management and customer analytics primary use cases
Media & Entertainment:
- 73% cloud adoption rate
- Content delivery and streaming infrastructure
- Real-time collaboration tools
Manufacturing:
- Most opportunistic growth segment during forecast period
- Real-time visibility and data management
- Integration of IoT, big data analytics, AI, and ML
- Supply chain optimization and enterprise resource planning
Healthcare:
- Projected 19.04% CAGR (highest among all sectors)
- $25.54 billion growth expected 2020-2025
- Telemedicine, AI diagnostics, and electronic health records
- Mobile health applications and wearable device integration
Government & Public Sector:
- 27.8% CAGR for government cloud market (2017-2025)
- Digital service delivery initiatives
- Data security and sovereignty requirements
- UAE and Middle East expansion in government cloud
Cloud Platform Market Share
Amazon Web Services (AWS):
- 32% global market share (largest provider)
- Early-mover advantage
- Most comprehensive service portfolio
- Dominant in startup and enterprise markets
Microsoft Azure:
- 21-23% market share
- 21% year-over-year growth (Q3 2025)
- Strong in enterprise due to Microsoft ecosystem integration
- Hybrid cloud leadership with Azure Arc and Azure Stack
Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
- 12% market share
- AI/ML and data analytics leadership
- Kubernetes and container orchestration strength
- Fastest growth in data-centric companies
Alibaba Cloud:
- 3rd globally, #1 in Asia-Pacific
- Regional dominance in growing markets
Other Providers:
- Oracle, IBM, Salesforce significant in niche markets
- 54% of users rely on three or more cloud storage providers
- Multi-cloud strategy increasingly common
Skills Gap and Opportunity Analysis
The Critical Shortage
Quantified Gap:
- 90%+ organizations facing IT skills shortages by 2026
- $5.5 trillion estimated global cost
- Cloud skills among most critically needed
- 65% of organizations abandoned AI projects due to skills shortage
Skills Evolution Rate:
- AI-exposed roles evolving 66% faster than traditional positions
- Continuous learning essential for career sustainability
- Rapid technology advancement outpacing workforce development
Most Sought-After Technical Skills
Platform Knowledge:
- AWS (most demanded)
- Microsoft Azure (enterprise focus)
- Google Cloud Platform (data/AI specialization)
DevOps Practices:
- Infrastructure as Code (Terraform, CloudFormation)
- CI/CD pipeline development
- Container orchestration (Kubernetes, Docker)
- Configuration management
Cloud-Native Technologies:
- Serverless computing (Lambda, Azure Functions)
- Microservices architecture
- Service mesh implementations
- API gateway management
Security Expertise:
- Zero-trust architecture
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Cloud compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, FedRAMP)
- Data encryption and key management
Data & Analytics:
- Big data processing (Spark, Hadoop)
- Data pipeline design
- Machine learning model deployment
- Real-time analytics
Emerging Specializations:
- Edge computing
- Multi-cloud management
- FinOps and cloud cost optimization
- AI/ML integration
- Kubernetes administration

Experience vs. Certification
Career Entry Points:
For Fresh Graduates:
- Foundational certifications open entry-level positions
- AWS Cloud Practitioner, Azure Fundamentals, GCP Digital Leader
- Expected starting salary: $80,000-$110,000
- 40% salary increase reported after first cloud certification
For Career Switchers:
- Associate-level certifications demonstrate capability
- AWS Solutions Architect Associate, Azure Administrator (AZ-104)
- Hands-on project portfolio critical
- 3-6 months preparation typical for career transition
For Experienced IT Professionals:
- Professional/expert certifications for advancement
- Specialization in security, data, or architecture
- Senior positions require 3-5 years cloud experience
- Certification plus experience yields highest ROI
Realistic Career Challenges
Market Competition
Competitive Landscape:
- High demand creates influx of new professionals
- 81% of U.S. engineering leaders hiring globally
- Increased competition from international talent pools
- Differentiation requires specialization and continuous learning
Entry Barriers:
- Foundational knowledge accessible to beginners
- Professional roles require demonstrable hands-on experience
- Catch-22: Need experience to get hired, need job to gain experience
- Solution: Personal projects, open-source contributions, labs
Technology Evolution Pace
Continuous Learning Imperative:
- Cloud platforms release new services quarterly
- Serverless, edge computing, AI integration rapidly evolving
- Skills depreciate without regular updating
- Professional development time investment: 5-10 hours weekly
Certification Maintenance:
- AWS certifications valid 3 years
- Azure certifications valid 1-2 years
- Recertification requires current knowledge demonstration
- Ongoing education costs ($100-$500 per certification)
Work Demands
On-Call Requirements:
- Cloud infrastructure runs 24/7
- Many positions include on-call rotation
- Incident response expectations
- Work-life balance varies by employer
Multi-Cloud Complexity:
- Organizations adopting 2-3 cloud platforms simultaneously
- Need proficiency across multiple ecosystems
- Each platform has unique services and terminology
- Increased cognitive load and learning requirements
Security Pressure:
- Data breach consequences severe
- High-stakes responsibility
- Regulatory compliance complexity
- Continuous security threat evolution
Geographic Considerations
Location Impact:
- Highest salaries concentrated in tech hubs
- Cost-of-living offsets salary premiums
- Remote work normalizing but not universal
- Some roles require on-site presence for security
Global Competition:
- Cloud work highly portable
- Companies hiring internationally
- Wage arbitrage pressure in some segments
- Specialized skills less vulnerable to outsourcing
Organizational Challenges
Legacy System Integration:
- Cloud migration projects complex
- Technical debt management
- Organizational resistance to change
- Political navigation required
Budget Constraints:
- FinOps pressure to optimize spending
- Cost management increasingly critical skill
- Performance vs. cost trade-offs
- Justification of cloud investments to leadership
Practical Career Roadmap
Phase 1: Foundation Building (0-3 Months)
Knowledge Acquisition:
- Choose Primary Platform (AWS recommended for beginners due to market share)
- Alternative: Azure for Microsoft-heavy environments
- Alternative: GCP for data/AI career focus
- Free Learning Resources:
- AWS Training and Certification free digital courses
- Microsoft Learn for Azure
- Google Cloud Skills Boost
- YouTube channels: A Cloud Guru, Linux Academy content
- Core Concepts to Master:
- Cloud computing models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
- Shared responsibility model
- Virtualization fundamentals
- Networking basics (VPC, subnets, security groups)
- Storage types and use cases
- Identity and access management
- Hands-On Practice:
- Create free-tier account (AWS, Azure, GCP all offer free tiers)
- Deploy simple web application
- Set up virtual machines
- Configure basic networking
- Implement simple storage solutions
- Track with documentation/blog posts
Investment:
- Time: 10-15 hours weekly
- Cost: $0-50 (free tier covers most learning)
Phase 2: Certification Achievement (3-6 Months)
Entry-Level Certification:
AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner (CLF-C02):
- Cost: $100
- Recommended study time: 40-60 hours
- Pass rate: 65-70% with preparation
- Validates: Cloud concepts, AWS architecture, security, billing
OR
Microsoft Azure Fundamentals (AZ-900):
- Cost: $99
- Study time: 30-50 hours
- Ideal for: Enterprise career focus
OR
Google Cloud Digital Leader:
- Cost: $99
- Study time: 30-50 hours
- Ideal for: Data and AI focus
Preparation Strategy:
- Official study guide (free from provider)
- Practice exams (Udemy, Whizlabs: $10-30)
- Hands-on labs concurrent with study
- Join study groups (Reddit, Discord communities)
- Schedule exam with 2-week buffer
Portfolio Development:
- Document 3-5 projects on GitHub
- Create technical blog explaining learnings
- Participate in cloud community forums
- Contribute to open-source cloud projects
Investment:
- Time: 15-20 hours weekly
- Cost: $100-200 (certification + study materials)
Phase 3: Job Market Entry (6-9 Months)
Resume Optimization:
Key Elements:
- Certification prominently displayed
- Projects with technical detail
- Quantifiable achievements (“Reduced deployment time by 40%”)
- Relevant keywords (AWS, Azure, Kubernetes, Terraform, Docker, CI/CD)
- GitHub profile link with active projects
Target Positions:
- Junior Cloud Engineer
- Cloud Support Engineer
- DevOps Engineer (entry-level)
- Systems Administrator (cloud-focused)
Job Search Strategy:
- LinkedIn profile optimization with certifications
- Indeed, Dice, AWS Jobs, Azure Careers job boards
- Company career pages (AWS, Microsoft, Google hire extensively)
- Networking: Attend cloud meetups, AWS User Groups
- Recruiters: Cloud-specialized technical recruiters
Interview Preparation:
- Technical fundamentals review
- System design basics
- Behavioral questions (STAR method)
- Hands-on troubleshooting scenarios
- Salary negotiation research
Expected Outcomes:
- Entry salary: $80,000-$110,000
- Geographic variation applies
- Startup vs. enterprise trade-offs
- Remote opportunities expanding
Investment:
- Time: 10-15 hours weekly (job search + preparation)
- Cost: $0-50 (resume services optional)
Phase 4: Professional Advancement (9-24 Months)
Associate-Level Certification:
AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate:
- Cost: $150
- Study time: 60-100 hours
- Salary impact: +$15,000-$30,000
- Coverage: Architecture design, security, cost optimization
OR
Azure Administrator Associate (AZ-104):
- Cost: $165
- Study time: 60-100 hours
- Enterprise focus
OR
Google Professional Cloud Architect:
- Cost: $200
- Study time: 80-120 hours
- Highest-paying certification path
Career Development:
- Take ownership of projects at work
- Cross-train on secondary cloud platform
- Develop specialization (security, data, networking)
- Mentor junior colleagues
- Present at internal tech talks
Skill Expansion:
- Infrastructure as Code (Terraform mastery)
- Advanced networking
- Kubernetes administration
- Cloud security frameworks
- Multi-cloud management
Investment:
- Time: 10-15 hours weekly (study + skill development)
- Cost: $150-300 (certification + advanced courses)
Phase 5: Specialization & Leadership (24+ Months)
Professional/Expert Certification:
Choose specialization path:
Architecture Track:
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Professional ($300)
- Azure Solutions Architect Expert (AZ-305) ($165)
- Average salary: $155,000-$175,000
Security Track:
- AWS Certified Security – Specialty ($300)
- Azure Security Engineer (AZ-500) ($165)
- CCSP (Certified Cloud Security Professional) ($445)
- Average salary: $150,000-$182,000
Data/AI Track:
- Google Professional Data Engineer ($200)
- AWS Certified Machine Learning – Specialty ($300)
- Average salary: $160,000-$185,000
DevOps Track:
- AWS Certified DevOps Engineer – Professional ($300)
- Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) ($395)
- Average salary: $145,000-$170,000
Leadership Development:
- Technical team lead opportunities
- Architecture review board participation
- Mentorship of junior engineers
- Conference speaking
- Technical writing and thought leadership
Investment:
- Time: 5-10 hours weekly (continuous learning)
- Cost: $300-500 annually (certifications, conferences, courses)

Alternative Pathways
Bootcamp Route:
- Intensive 12-16 week programs
- Cost: $10,000-$15,000
- Faster entry but requires full-time commitment
- Career services and placement support
- Examples: General Assembly, Flatiron School
University Programs:
- Cloud computing certificates (6-12 months)
- Cost: $3,000-$8,000
- Example: University of Virginia SCPS Cloud Computing Certificate
- Academic rigor and networking
- Career services included
Self-Paced Online Platforms:
- A Cloud Guru subscriptions: $29-$47/month
- Linux Academy, Pluralsight, Coursera
- Flexibility for working professionals
- Comprehensive learning paths
Time Investment Summary
Minimum viable timeline:
- Foundation to first job: 6-9 months (aggressive, full-time focus)
- Typical timeline: 9-12 months (part-time while working)
- Senior position: 3-5 years total experience
Weekly time commitments:
- Beginning: 10-15 hours
- Certification prep: 15-20 hours
- Continuous learning (career-long): 5-10 hours
Certification Path and ROI
Certification Economics
Investment Analysis:
Entry-Level Certification:
- Cost: $99-$100
- Preparation time: 40-60 hours
- Salary increase: $10,000-$20,000 first year
- ROI timeline: 1-2 months of increased earnings
Associate-Level Certification:
- Cost: $150-$165
- Preparation time: 60-100 hours
- Salary increase: $15,000-$30,000
- ROI timeline: 1-2 months
Professional-Level Certification:
- Cost: $200-$300
- Preparation time: 100-150 hours
- Salary increase: $20,000-$40,000
- ROI timeline: 1-3 months
Lifetime Value:
- Average cloud professional career span: 15-20 years
- Certification-driven salary premium: 25-40% throughout career
- Total career earnings impact: $300,000-$600,000
- Initial investment: $500-$1,500 (all certifications)
Platform Selection Guide
Choose AWS if:
- Maximum job market availability desired
- Startup or broad industry focus
- North American job market primary target
- Most comprehensive certification ecosystem
Choose Azure if:
- Enterprise/corporate environment preference
- Existing Microsoft ecosystem familiarity
- Government or highly regulated industry
- Strong in finance and insurance sectors
Choose GCP if:
- Data engineering or AI/ML career focus
- Innovation-focused companies preferred
- Kubernetes and container expertise desired
- Highest average certification salaries
Multi-Cloud Strategy:
- Learn one platform deeply first (12-18 months)
- Add second platform at associate level (6-12 months later)
- Third platform for senior/architect roles
- Specialist certification in one, generalist knowledge in others
Certification Progression Paths
Recommended Sequence for Cloud Engineer:
- Foundation (Month 1-3): AWS Cloud Practitioner or Azure Fundamentals
- Core Competency (Month 6-9): AWS Solutions Architect Associate or Azure Administrator
- Specialization (Month 18-24): Choose track (Architecture, Security, DevOps, Data)
- Mastery (Month 30-36): Professional-level certification in specialty
- Leadership (Ongoing): Continuous learning, multi-cloud, emerging technologies
Recommended Sequence for DevOps Engineer:
- Foundation (Month 1-3): AWS Cloud Practitioner
- Infrastructure (Month 6-9): AWS Solutions Architect Associate
- Container Orchestration (Month 12-18): Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA)
- Advanced DevOps (Month 24-30): AWS DevOps Engineer Professional
- Infrastructure as Code (Optional): HashiCorp Terraform Associate
Recommended Sequence for Security Specialist:
- Foundation (Month 1-3): AWS Cloud Practitioner or Azure Fundamentals
- Core Competency (Month 6-9): AWS Solutions Architect Associate or Azure Administrator
- Security Focus (Month 18-24): AWS Security Specialty or Azure Security Engineer (AZ-500)
- Professional Certification (Month 30-36): CCSP (Certified Cloud Security Professional)
- Compliance (Optional): Vendor-specific compliance certifications
Certification Maintenance
Recertification Requirements:
AWS:
- Validity period: 3 years
- Renewal: Pass current version or higher-level exam
- Continuing education credits alternative
- Cost: Same as initial certification
Azure:
- Validity period: 1-2 years (role-dependent)
- Renewal: Free online assessment annually
- Must stay current with role requirements
- No additional cost for renewal
Google Cloud:
- Validity period: 2 years
- Renewal: Retake current exam
- No continuing education alternative
- Cost: Same as initial certification
Strategy:
- Build recertification into annual professional development
- Stack certifications to distribute renewal burden
- Use recertification as learning opportunity
- Budget time and money for ongoing maintenance
Final Verdict: Is Cloud Computing a Hot Skill?
Quantitative Evidence Summary
Market Growth:
- ✅ $912.77 billion market (2025) growing to $5,946.84 billion (2035)
- ✅ 20.61% compound annual growth rate
- ✅ All forecasting models show consistent double-digit growth
- ✅ No signs of market saturation through 2035
Job Demand:
- ✅ 25-26% employment growth (vs. 4% average for all occupations)
- ✅ 317,700 annual job openings
- ✅ 451,000 new positions expected next decade
- ✅ 90%+ organizations facing skills shortage
Compensation:
- ✅ $138,000 median total compensation (national average)
- ✅ $80,000-$110,000 entry-level salaries
- ✅ $175,000+ senior-level compensation
- ✅ 25-40% salary premium for certified professionals
Industry Adoption:
- ✅ 96% of companies use public cloud
- ✅ 80% operate multi-cloud strategies
- ✅ All major industries investing heavily in cloud infrastructure
- ✅ Government, healthcare, finance, manufacturing accelerating adoption
Skills Gap:
- ✅ $5.5 trillion cost of IT skills shortage
- ✅ 90%+ organizations cannot fill cloud positions
- ✅ Supply-demand imbalance favoring job seekers
- ✅ Shortage projected to continue through 2030s
Qualitative Assessment
Career Sustainability:
- Long-term viability: Excellent. Cloud infrastructure underpins modern digital economy. Not a passing trend.
- Technology evolution: Continuous but manageable. Skills transferable across platforms and versions.
- Industry diversity: Present in all sectors from healthcare to retail to government.
- Geographic flexibility: Remote work common. Opportunities in all major markets.
Career Satisfaction Factors:
- Intellectual challenge: High. Continuous problem-solving and learning.
- Impact visibility: Clear connection between work and business outcomes.
- Innovation opportunity: Working with cutting-edge technologies (AI, ML, edge computing).
- Team collaboration: Cross-functional work with developers, security, operations.
Risk Factors:
- Competition: High demand attracts many entrants. Differentiation required.
- Continuous learning: Non-negotiable time investment throughout career.
- Automation: Some routine tasks being automated, but complexity increasing overall.
- Market consolidation: Three providers dominate, though multi-cloud creates opportunities.
Decision Framework for Career Seekers
Cloud computing is ideal for you if:
✅ You enjoy problem-solving and technical challenges
✅ Continuous learning appeals rather than intimidates
✅ You want to work across multiple industries
✅ Remote work flexibility is important
✅ Above-average compensation is a priority
✅ You’re comfortable with on-call responsibilities
✅ You prefer practical, hands-on work over pure theory
✅ You want to work with emerging technologies (AI, ML, IoT)
Consider alternatives if:
❌ You prefer slow-changing, stable technology environments
❌ Work-life balance with zero after-hours work is non-negotiable
❌ You dislike continuous learning and recertification
❌ You want highly specialized work that doesn’t change
❌ You’re uncomfortable with high-stakes system responsibility
❌ You prefer predictable, routine daily tasks
Verdict for Different Career Stages
For Students (High School/College):
- Recommendation: Strong YES
- Rationale: Ground-floor opportunity in growth industry. Entry barriers manageable with certifications. 20-30 year career runway with technology that will dominate their working lifetime.
- Action: Begin with foundational certification. Pursue internships at cloud-forward companies. Consider a computer science degree with cloud specialization.
For Recent Graduates:
- Recommendation: Strong YES
- Rationale: Perfect timing to enter high-demand field. Certifications can differentiate in a competitive entry-level market. Student debt offset by above-average starting salaries.
- Action: Achieve associate-level certification within 6 months. Target cloud engineer or DevOps positions. Accept entry role to gain experience even if slightly lower salary.
For Career Switchers (3-10 years experience):
- Recommendation: YES with conditions
- Rationale: Strong demand and good salaries, but requires 6-12 month investment to become competitive. Must be willing to potentially take lateral salary move initially for long-term gain.
- Action: Assess transferable skills (networking, programming, systems administration). Pursue bootcamp or intensive self-study. Target roles that bridge current experience with cloud.
For Mid-Career Professionals (10+ years experience):
- Recommendation: YES for IT professionals, MAYBE for non-IT
- Rationale: Existing IT experience highly valuable. Can fast-track to senior positions. However, starting from zero requires significant investment with a shorter career runway.
- Action: If in IT, add cloud certifications to existing expertise. If non-IT, carefully assess opportunity cost of career change versus ROI given fewer working years remaining.
Conclusion: The Data Speaks Clearly
Is cloud computing a hot skill in 2026? The answer is an unequivocal YES.
Every quantitative metric confirms exceptional opportunity:
- Market growing at 20%+ annually through 2035
- 26% job growth rate (6.5x faster than average)
- $138,000 median compensation with strong growth trajectory
- Critical skills shortage creating seller’s market for talent
- Universal industry adoption eliminating sector risk
The data shows cloud computing is not merely “hot” but represents a fundamental shift in how technology infrastructure operates. This is not a trend but a transformation that will define the next two decades of computing.
For career decision-makers and students: Cloud computing offers a rare combination of high demand, excellent compensation, intellectual challenge, and long-term career sustainability. The barriers to entry are manageable, the learning curve is navigable, and the ROI on certification investment is exceptional.
The question is not whether cloud computing is a valuable skill to acquire in 2026, but rather which cloud platform and specialization aligns best with your career goals.
The opportunity window is open. The data supports action. The time to begin is now.






